Statistics Explained
Statistics refers to the organization, analysis and presentation of data to derive useful information and trends (James, Witten, Hastie, & Tibshirani, 2013). The data to be analyzed comes in different forms. Broadly, there are two main kinds of data: qualitative(nominal or ordinal), and quantitative (numerical).
There exists two main types of statistics namely descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. Descriptive statistics uses the measures of central tendency (mean, mode, and median) to describe a population (Peersman, 2014). Besides, they use measures of spread like standard deviation, variance, range, skewness and kurtosis to describe the spread of the data. The mean represents an arithmetic average of the data (sum of all observations divided by the number of observations (James, Witten, Hastie, & Tibshirani, 2013). Also, the median is the middle most value when arranged in ascending/ descending order. The mode refers to the most frequent observation.
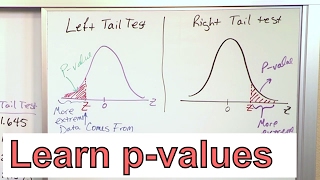
Inferential statistics enable the researcher to infer and make generalkisations about a population. They include correlation, regression, ttest, Analysis of variance (ANOVA), for numerical variables (Smith, 2018). In addition, it includes Chi square test, spearman’s correlation test ManWhitnesy test among others for qualitative data (Smith, 2018). All these tests depend on the test statistic and the p value to make inferences



![Descriptive Statistics [Simply explained]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/FzujIYo9GYo/mqdefault.jpg)