Why Are Capacitors on Motors? What is Capacitive Reactance and Inductive Reactance?
Most of us know what a motor is. But what about capacitors? And why would we need them to be on a motor? In the latest episode of Electrician U, Dustin answers discusses why we would need to have capacitors on our motors.
⚡MEMBERSHIP⚡
JOIN ELECTRICIAN U become a member and get:
FREE Continuing Education every year
FREE Practice Exams
FREE Monthly Video Courses
FREE Weekly Live InstructorLed Classes
FREE Monthly Educational Newsletter
Premium MembersOnly Content
Private Discord Channel
Monthly MembersOnly Discord Chats
Sign up here https://www.electricianu.com/electric...
MUSIC AND VIDEO:
/ descantmv
✍ART AND ILLUSTRATION:✍
https://www.daverussoart.com
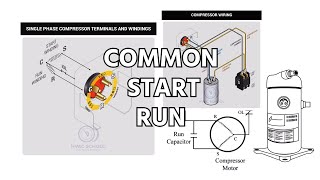
Capacitors for the most part are an energy storage device. They will charge up and store energy and then discharge when its needed. But why would we need that for a motor? To answer that, we need to understand how a motor starts when power is applied to it. If we had the leads for the motor connected and the motor poles are in line, the motor will turn until those points are no longer in line. But the power points are now out of sequence (in a sense) and the motor can no longer spin. What a capacitor does is provide a charge to bump those points so they are back in line and the applied voltage can cause them to spin again.
There are also a couple of terms that we need to know when discussing capacitors. Those are inductive reactance and capacitive reactance. Inductive reactance is where the voltage is leading, and current is lagging. In capacitive reactance is where Current leads and Voltage lags. In essence, in an inductive circuit, the amount of magnetic energy keeps things so bound up that it slows down the current flow. However, the voltage is still churning away, but the current is lagging. In a capacitor, when discharged, the positive and negative are just randomly kind of hanging out together. But when charged, those positive charges group together, as do the negatives, in a much more orderly fashion, ready to be discharged to do their work. But with them being so far apart now, current cannot get thru, hence the current LAG in capacitive reactance! In essence, inductive and capacitive are just polar opposites of one another.
In many motors there are actually 2 capacitors. A start capacitor and a run capacitor. The start capacitor is used to get the motor spinning as this usually requires a much larger push. Once the motor has taken off and churning along, then the run capacitor takes over. The run capacitor still provides the same function in keeping the motor shaft spinning when its not inline with the motor leads, just not as much is needed as the force of the shaft moving helps it along.
Capacitors are also used to keep things from being so lopsided. They smooth the process out a bit. In lieu of there being such a large Voltage draw every other cycle, and none on the opposing, capacitors smooth that up and down action. This tends to make the process much smoother and less jerky!
There are also other flavors of capacitors that provide both start AND run functions as well as capacitors that can provide either the Start or Run functions for multiple motors.
We hope this has been an insightful look into inductive/capacitive reactance and why we need capacitors on motors. Is there a topic you would like to see discussed on Electrician U? Leave a comment in the comments section and let us know. Please continue to follow Dustin and Electrician U as we are constantly updating our content to assist our followers in becoming the best electricians that they can be!
#electrician #electrical #electricity #capacitors explained #capacitive reactance #inductive reactance #customers questions