Mastering S3 and S4 | Learn Third and Fourth Heart Sounds🫀
#drnajeeb #medicaleducation #drnajeeblectures #cardiology
Mastering S3 and S4 | Learn Third and Fourth Heart Sounds
Like this video? Sign up now on our website at https://www.DrNajeebLectures.com
to access 800+ Exclusive videos on Basic Medical Sciences & Clinical Medicine. These are premium videos (NOT FROM YOUTUBE). All these videos come with English subtitles & download options. Sign up now! Get Lifetime Access for a onetime payment of $99 ONLY!
Sign up now on our website at https://members.drnajeeblectures.com/...
Why sign up for premium membership? Here's why!
Membership Features for premium website members.
1. More than 800+ Medical Lectures.
2. Basic Medical Sciences & Clinical Medicine.
3. Mobilefriendly interface with android and iOS apps.
4. English subtitles and new videos every week.
5. Download option for offline video playback.
6. Fanatic customer support and that's 24/7.
7. Fast video playback option to learn faster.
8. Trusted by over 2M+ students in 190 countries.
▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬ Contents of this video ▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
00:00:00 Introduction and brief review on first and second heart sounds S1 & S2
00:05:11 Genesis of 3rd Heart Sound (early diastole)
00:15:23 Diastasis
00:19:12 Genesis of 4th Heart Sound (late diastole, always pathological)
00:26:13 Recap
Pattern of sounds
00:27:58 S3 gallop, ventricular gallop, early diastolic gallop
00:29:14 b) S4 gallop, atrial gallop, late diastolic gallop
00:37:21 c) Quadruple gallop
00:40:10 d) Summation gallop
00:44:28 Causes of S3 heart sound
00:52:01 Causes of S4 heart sound
00:58:54 Review
The third and fourth heart sound (S3 and S4) are two abnormal heart sound components which are proved to be indicators of heart failure during diastolic period. The combination of using diastolic heart sounds with the standard ECG as a measurement of ventricular dysfunction may improve the noninvasive diagnosis and early detection of myocardial ischemia.
Heart sounds are produced from a specific cardiac event such as closure of a valve or tensing of a chordae tendineae.
Many pathologic cardiac conditions can be diagnosed by auscultation of the heart sounds. Note that heart sounds are discrete, short audible events from a specific cause — different from a heart murmur. A murmur is due to turbulence of blood flow and can, at times, encompass all of systole or diastole.
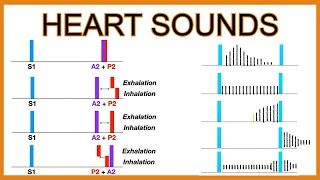
The main normal heart sounds are the S1 and the S2 heart sound. The S3 can be normal, at times, but may be pathologic. A S4 heart sound is almost always pathologic. Heart sounds can be described by their intensity, pitch, location, quality and timing in the cardiac cycle.
Intensity: Heart sounds can be described as increased in intensity (loud), decreased in intensity (soft) or absent.
Pitch: Heart sounds can be described as high pitched (heard best with the diaphragm of the stethoscope).
Location: The location of the heart sound can help determine the etiology. The standard listening posts (aortic, pulmonic, tricuspid and mitral) apply to both heart sounds and murmurs. For example, the S1 heart sound — consisting of mitral and tricuspid valve closure — is best heard at the tricuspid (left lower sternal border) and mitral (cardiac apex) listening posts.
Timing: The timing can be described as during early, mid or late systole or early, mid or late diastole.
Although terms such as “click,” “snap” or “knock” are sometimes used, they have no specific quality or meaning. They will be referenced in the following sections.
Join this channel to get access to perks:
Sign up now on our website at https://members.drnajeeblectures.com/...
/ @doctornajeeb
Follow us on Facebook : / drnajeeb
Follow us on Instagram : / drnajeeblectures