Knee Pain Meniscus tear - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes knee pain examination of the meniscus.
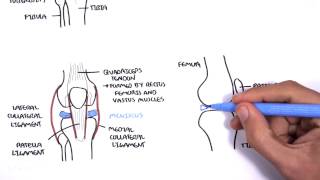
There is two types of cartilage between the femur and tibia:
• Articular cartilage
• Meniscus cartilage
And there is a meniscus in between.
The meniscus is a fibrocartilage structure that carries type I collagen, it is triangular shaped in cross section.
There are two menisci:
• Lateral meniscus:more mobile that the medial meniscus
Circular
Covers about 70% of the lateral tibial plateau
• Medial meniscus: its tears occur about three times more than that of the lateral meniscus
Cshaped
Covers about 50% of the medial tibial plateau
Function:
• Shock absorption
• Load sharing
• Joint stability
Meniscal tear causes:
• Twisting, jumping, or changing directions during sports activities such as skiing or football.
• Degenerative tears of the medial meniscus may occur in older patients.
• Degenerative tears may occur in association with arthritis.
Symptoms of the meniscal tear:
Pain on the medial or lateral side of the knee
Mechanical symptoms:
Locking
Clicking
Swelling
Examination:
Joint line tenderness is the most sensitive exam; posterior knee pain may also be present when the knee is bent.
Look for the knee joint effusion, effusion may be difficult to find and occur several hours to appear after the injury.
With ACL tears, the hemorrhage and swelling is greater and develops rapidly.
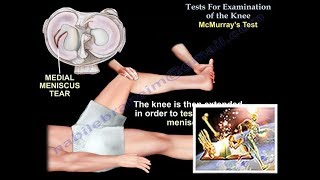
Mcmurray’s test is used to diagnose meniscal tear, a painful pop or click is obtained as the knee is brought from flexion to extension with either internal or external rotation of the knee.
To test the medial meniscus, flex the knee and place the hand on the medial aspect of the knee.
The knee is then extended in order to test the medial meniscus.
Feel a pop or click with knee extension, the patient will experience pain.
A positive test is indicated by pain, clicking, or popping within the joint and may signal a tear of the medial meniscus.
To diagnose the lateral meniscus tear, do the Mcmurray’s test with internal rotation of the knee.
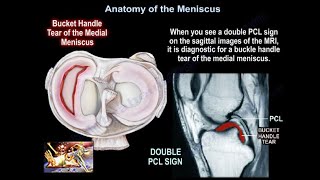
Sometimes the knee is locked with lack of full extension due to a bucket handle tear of the meniscus.
Differential diagnosis:
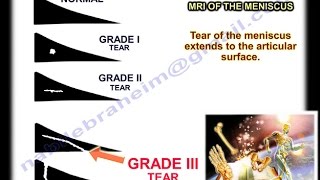
• The clinical diagnosis accuracy of meniscal tear is about 70%.
• MRI is usually done to confirm the diagnosis or identify other problems in the knee.
• The differential diagnosis can be intraarticular problems or extraarticular problems.
• Intraarticular problems:
Medial synovial plica irritation.
Osteochondritis lesions (OCD).
Patellofemoral pain
Loose bodies
• Extraarticular problems:
Collateral ligament injury, especially the medial collateral ligament
Pes anserine bursitis
Lumbar disc herniation
Stress fracture
Iliotibial band syndrome
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE).
Blood supply:
The meniscus receives blood supply from the genicular vessels and its capsular attachment.
The peripheral 1/3 area is the most vascularized area and tears within this area usually heal.
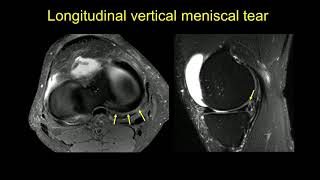
Where is the tear located?
Treatment of meniscal tears:
• Nonoperative:
Especially for small nondisplaced tears and degenerative tears.
Physiotherapy
NSAIDS
With persistence of symptoms, cortisone injection may be given.
When the conservative treatment fails, then do surgery.
• Surgery:
Excision of the tear (partial meniscectomy): you do excision if the tear is complex, degenerative, or if it is a radial tear that cannot be repaired.
Repair of the meniscal tear: usually done for a peripheral tear which is vascular and will heal.
It is better to have the combination of repair of the meniscus at the same time you do ACL reconstruction (controversial).
Meniscal transplant: done in younger patients who had total meniscectomy (especially lateral meniscus).
It takes about one year for the graft to heal.
Retear of the transplanted meniscus is also common.
If you do total meniscectomy, this will probably lead to future arthritis of the knee.
Special situations:
• In general, medial meniscal tears occur more often than tear of the lateral meniscus.
In older patients, the posterior horn of the medial meniscus is usually more often affected.
• With ACL tears that are acute, then there will be more incidences of lateral meniscal tears.
• With ACL tears that are chronic, then there will be more incidences of medial meniscal tears.
• With tibial eminence fractures in children, the medial meniscus can become trapped in this injury.
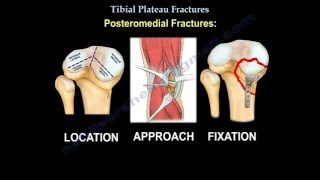
• Tibial plateau fractures:
If the injury is medial then it can affect the medial meniscus.
If the injury is lateral then it can affect the lateral meniscus.
• If you have depression or displacement separation more than 5 mm, you can have meniscal injury.
Discoid meniscus: the meniscus is usually larger than normal and occurs more in the lateral meniscus, the treatment is usually saucerization plus or minus repair of the lateral meniscus if symptomatic.