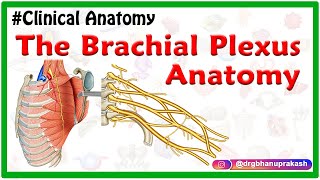
Epithelial tissue : Squamous cuboidal columnar Simple stratified pseudostratified transitional
: / drgbhanuprakash
: https://t.me/bhanuprakashdr
: https://linktr.ee/DrGBhanuprakash
Epithelial tissue : Squamous, cuboidal, columnar, Simple, stratified, pseudostratified, transitional
Epithelial tissue serves important roles for protection, absorption, and secretion.
Epithelial tissue can be organized into layers or into glands, collections of cells that specialize in secreting different products.
Epithelial cells rest on an underlying basal lamina, which together with the reticular lamina constitutes the basement membrane.
Epithelium is classified by the shape of the uppermost layer of cells, which can be squamous, cuboidal, or columnar.
Epithelium is also classified by the number of cell layers: simple (one layer), stratified (more than one layer), and pseudostratified (falsely appearing to be stratified).
Some lining epithelial cells have apical surface modifications that include microvilli (specialized for absorption and secretion), cilia (motile extensions found in the respiratory tract and fallopian tubes), and stereocilia (long microvilli specialized for absorption).
Glands are either exocrine or endocrine; exocrine glands secrete onto epithelial surfaces through ducts, while endocrine glands secrete their products into blood vessels.
Endocrine glands secrete their products, called hormones, into the blood for circulation to target organs. Exocrine glands secrete their products onto epithelial cell surfaces like the GI tract or skin.
Exocrine glands can be classified based on structure (unicellular vs multicellular), type of secreted product (serous or mucus), and method of secretion (eccrine, holocrine, or apocrine).
Intercellular junctions connect epithelial cells to each other and to the basement membrane and also facilitate intercell communication and modulate passage of substances between the cells.
The types of intercellular junctions are belt desmosomes, spot desmosomes, hemidesmosomes, gap junctions, and tight junctions.
#epithelialtissue #epithelialtissuehistology #epithelialtissuetypes #epithelialtissueclassification #histology #usmle #mbbs #neetpg #nationalexittest #nationalexitexam #usmlestep1