CN 10: Vagus Nerve (Scheme Pathway Branches) | Neuroanatomy
Content:
Introduction 0:00
Vagus Nerve Scheme 00:49
Functional Components 10:46
Nuclei of Vagus Nerve 14:01
Intracranial Course 15:30
Extracranial Course 15:57
Branches of the Vagus Nerve 17:32
Branches in the Jugular Fossa 17:52
Branches in the Neck 19:00
Branches in the Thorax 24:51
Branches in the Abdomen 27:41
Recap 30:11
Channel membership: / @taimtalksmed
Follow my IG: / taimtalksmed
Donation link: https://www.buymeacoffee.com/taimtalk...
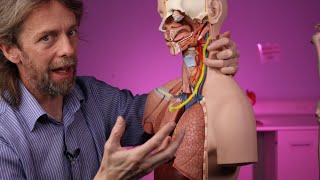
Longest course of all the cranial nerves, extending from the head to the abdomen it has a parasympathetic component, which help regulate functions like the heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate. It has sensory component to relay information from various visceral organs, and a motor component for tasks like speech and swallowing.
Functional Components of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve:
Special visceral efferent fibers (SVE) (somatomotor fibers of vagus nerve)
General visceral efferent fibers (GVE) (visceral motor fibers of vagus nerve) provide parasympathetic innervation
General visceral afferent fibers (GVA) (visceral sensory fibers of vagus nerve)
Special Visceral afferent fibers (SVA).
General somatic afferent fibers (GSA) (general sensory) p
Nuclei of glossopharyngeal nerve:
Nucleus ambiguus motor
Posterior nucleus of vagus nerve (nucleus posterior nervi vagi)
Nuclei of solitary tract (nuclei tractus solitarii) – a viscerosensory nucleus
○ Gustatory nucleus (nucleus gustatorius) – a special sensory nucleus –
Spinal nucleus of trigeminal nerve (nucleus spinalis nervi trigemini) – a somatosensory nucleus
Course: Intracranial
Intracranial course:
The vagus nerve emerges as a series of rootlets in a groove between the olive and inferior cerebellar peduncle. It traverses the posterior cranial fossa and exits the skull through jugular foramen. The superior sensory ganglion of the nerve is located in the jugular foramen.
Extracranial course:
The inferior ganglion of vagus lies below the jugular foramen. Just below the inferior ganglion, cranial root of accessory nerve joins the vagus nerve to distribute along its pharyngeal and laryngeal branches. In the neck, vagus lies in the carotid sheath with the internal jugular vein and common carotid arteries. The right vagus runs on the posterior surface of oesophagus, contributing to the oesophageal plexus. It enters the abdomen by passing through the oesophageal opening in the diaphragm. It supplies stomach, duodenum, liver, kidneys, small and large intestine up to the junction of proximal twothirds and distal third of transverse colon. It has a wide distribution in the abdomen via coeliac, superior mesenteric and renal plexuses. The left vagus runs anterior to oesophageal plexuses, then enters abdomen supplies stomach, liver, duodenum and head of pancreas.
Branches in the jugular fossa:
Meningeal branch (ramus meningeus)
Auricular branch (ramus auricularis)
Branches in the neck
Pharyngeal branches (rami pharyngei)
○ Pharyngeal plexus (plexus pharyngeus)
Superior laryngeal nerve (nervus laryngeus superior)
○ Internal branch (ramus internus) – a sensory branch
○ External branch (ramus externus) a mixed branch
Recurrent laryngeal nerve (nervus laryngeus recurrens)
○ Tracheal branches (rami tracheales)
○ Esophageal branches (rami oesophagei)
○ Pharyngeal branches (rami pharyngei)
○ inferior laryngeal nerve (nervus laryngeus inferior)
○ Superior cervical cardiac branches (rami cardiaci cervicales superiores) forming cardiac plexus
Branches in thorax
Inferior cervical and thoracic cardiac branches (rami cardiaci cervicales inferiores et thoracici)
Bronchial branches (rami bronchiales)
○ Pulmonary plexus (plexus pulmonalis)
Oesophageal plexus (plexus oesophageus)
Branches in the abdomen
Anterior vagal trunk (Truncus vagalis anterior)
○ Anterior gastric branches (rami gastrici anteriores)
○ Hepatic branches (rami hepatici)
Posterior vagal trunk (Truncus vagalis posterior)
○ Posterior gastric branches (rami gastrici anteriores et posteriores)
○ Coelic branches (rami coeliaci)
§ Coeliac plexus (plexus coeliacus) or Solar Plexus
○ Renal branches (rami renales)
○ Hepatic branches (rami hepatici)
Sources:
Singh, I. (2017). Human neuroanatomy (10th ed.).
Kozlowski, T. (2017). Memorix Anatomy: The Complete Study Guide. 2nd ed. Thieme Medical Publishers.
Petko B, Tadi P. Neuroanatomy, Nucleus Ambiguus. [Updated 2023 Jul 24]. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan
Topography and extent of pulmonary vagus nerve supply with respect to transthoracic oesophagectomy. Journal of Anatomy,
Programs:
Complete Anatomy: https://3d4medical.com/
Biorender: https://www.biorender.com/
PowerPoint
Camtasia 2023
Pictures and Visuals used under licenced permission