Acute inflammation ( Vascular and cellular events ) Chronic inflammation Part 1: General Pathology
:https://telegram.me/bhanuprakashdr
: / drgbhanuprakash
: https://linktr.ee/DrGBhanuprakash
Acute inflammation and Chronic inflammation Part 1 : General Pathology
Acute inflammation
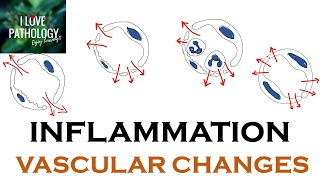
The three roles of inflammation are to deliver effector molecules, induce local clotting, and to promote tissue repair.
Neutrophils are the first immune cell to arrive at the site of injury or infection. Neutrophil response peaks about 24 hours after injury or infection.
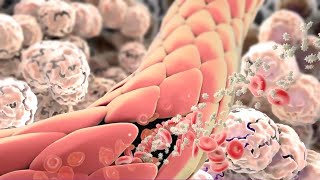
Leukocyte extravasation is a process that allows WBCs to exit the blood vessels and migrate to the site of injury or infection. This process involves four steps: margination and rolling, binding, diapedesis, and migration.
The cardinal signs of acute inflammation are pain (dolor), redness (rubor), heat (calor), and swelling (tumor).
Pharyngitis (sore throat) and bacterial pneumonia are common examples of acute inflammation.
Exudate is fluid that collects within tissues because of local inflammatory factors that lead to leukocyte extravasation and pus formation; this results in purulent inflammation.
Transudate is fluid pushed through the endothelial cells of vessel walls because of force imbalance in hydrostatic or oncotic pressure; this results in serous inflammation. Its composition is similar to that of serum.
Acute phase reactants are proteins such as Creactive protein, fibrinogen, serum amyloid A, ferritin, and hepcidin that can be measured in the blood or serum as indicators of inflammation.
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test is used to detect inflammation that may indicate cancer or the presence of infectious or autoimmune disease. It is measured in millimeters per hour and changes correlate with levels of serum fibrinogen.
Chronic inflammation
The four main causes of chronic inflammation are infection by resistant organisms, persistent injury, exposure to toxins, and autoimmune disease.
Chronic inflammation typically begins around 48 hours after injury and does not always display the classical signs of acute inflammation (redness, swelling, heat, pain).
Fibroblasts secrete collagen, a main component of connective tissue and a hallmark of chronic inflammation.
Macrophages, lymphocytes, and plasma cells are the main cell types involved in chronic inflammation.
Macrophages are responsible for consuming foreign substances and pathogens and orchestrating the response to injury.
T cells secrete cytokines that alter the behavior of other immune cells at the site of injury or infection.
Specialized B cells known as plasma cells create antibodies that target foreign pathogens for destruction.
Fibrosis is the replacement of damaged tissue with connective tissue that often impairs normal function.
Granulomas are clusters of macrophages that surround indigestible particles; they are considered a special form of chronic inflammation.
A fistula is an abnormal passageway between two hollow or tubular organs or between an organ and the body surface.
Crohn disease is characterized by chronic inflammation of the intestinal mucosa; fistulas are a major complication of Crohn disease.
Hepatic fibrosis impairs liver function; it occurs in hepatitis and chronic alcoholism.
Atherosclerosis is characterized by chronic inflammation of the vessel wall in response to endothelial damage, which leads to lipid accumulation in the vessel wall.
Fibrosis, angiogenesis, and tissue remodeling are potential consequences of chronic inflammation.
#inflammation #acuteinflammation #chronicinflammation #pathology #generalpathology #fmge #fmgevideos #rapidrevisionfmge #fmgejan2023 #mbbslectures #nationalexitexam #nationalexittest #neetpg #usmlepreparation #usmlestep1 #fmge #usmle #drgbhanuprakash #medicalstudents #medicalstudent #medicalcollege #neetpg2023 #usmleprep #pathologyvideos #pathologylectures #usmlepathology #neetpgpathology #fmgepathology